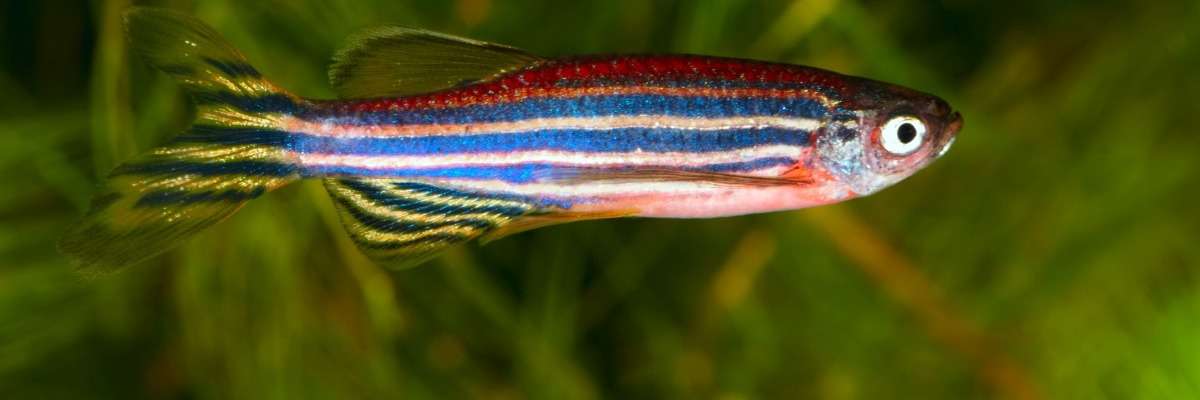
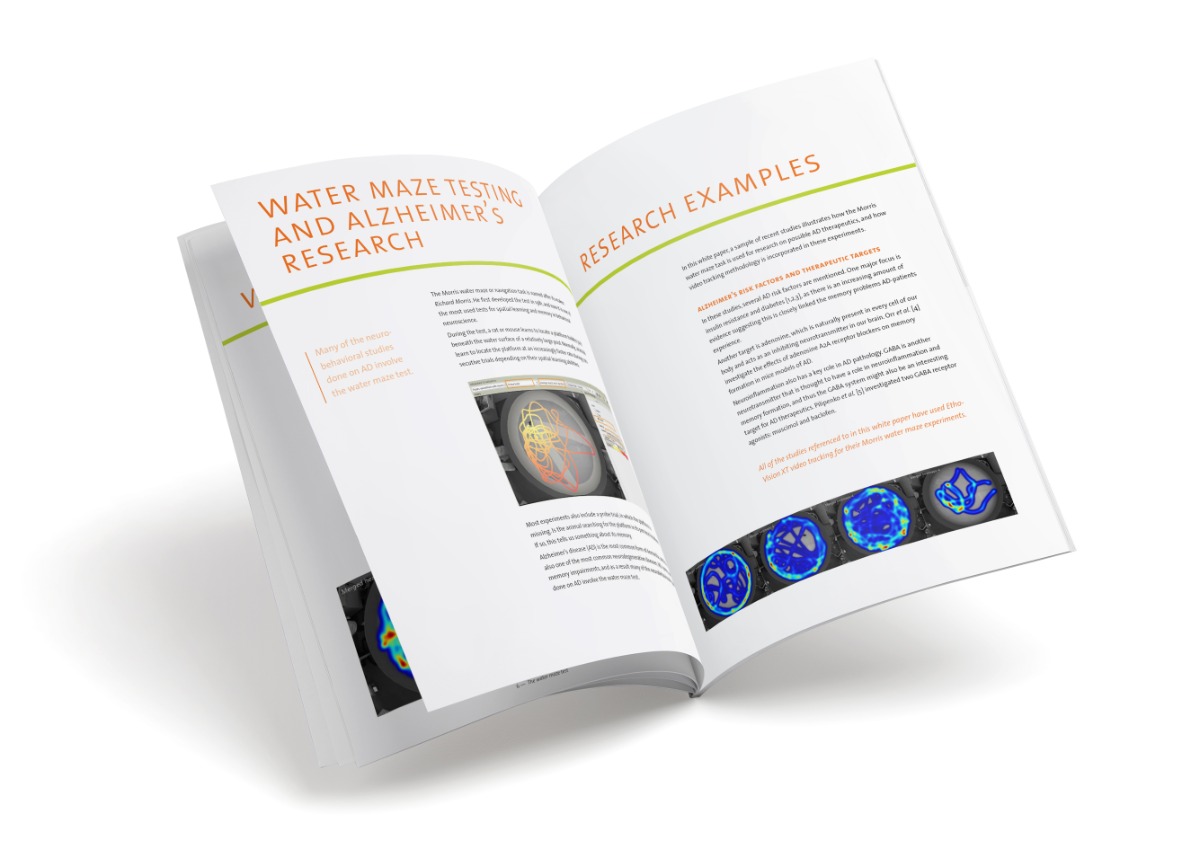
Zebrafish provide key insights into alcohol addiction
At this year's Neuroscience I talked to someone from the Gerlai Lab at the University of Toronto (Ontario) who is involved in very interesting research on alcohol addiction. That person was Steven Tran, and I am very happy to say that he agreed to share a story on our Behavioral Research Blog. Take it away, Steven!
Two and a Half Men’s Charlie Harper, although fictional, is the prototypical image of alcoholism. What makes individuals such as Charlie Harper different from the rest of us? Why is it that when people drink, only small subsets of individuals develop an alcohol addiction? Despite decades of research into alcohol addiction, the sad truth is that what we know about this debilitating disease is vastly outweighed by what we don’t know.
For example, we know that individuals that are more sensitive to the stimulant and pleasurable effects and less sensitive to the sedative and negative effects of alcohol are actually at a much higher risk of developing alcohol addiction. However, we don’t know what mechanisms underlie sensitivity to alcohol’s addictive effects, and to a larger extent, we don’t know the exact mechanisms through which alcohol acts on the brain or how individuals develop alcohol addiction.
Alcohol induced locomotor activity in zebrafish
The zebrafish brain, although anatomically different, exhibits evolutionarily conserved neurotransmitter systems which may allow us to study drug addiction pathways including alcoholism. The zebrafish is a small freshwater vertebrate which has been gaining traction in the behavioral sciences and specifically for investigating the neurochemical mechanisms underlying alcohol’s effects on the brain and behavior.
One of the simplest and arguably most relevant effects of alcohol examined in zebrafish is altered locomotor activity, which is easily quantified using EthoVision XT (Noldus), an automated video tracking software. Analysis of different animal models including rodents, fish and humans has suggested a link between alcohol’s stimulant effects and the development of alcohol addiction. However, the exact mechanisms in the brain underlying alcohol induced locomotor activity are not completely understood.

Neurochemical basis of alcohol induced locomotor activity
In the brain, neurons communicate with each other using neurochemical messages. Researchers at the University of Toronto Mississauga in the Gerlai lab use zebrafish to unravel the mysteries of alcohol addiction. Similar to humans and rodents, the neurochemical dopamine was found to play a large role in regulating alcohol’s locomotor stimulant effects in zebrafish.
For example, by inhibiting the rate-limiting enzyme that produces dopamine in vertebrates, including the zebrafish, researchers were able to reduce the locomotor stimulant effects of alcohol in zebrafish [1]. Likewise, when the receptors to which dopamine binds to were blocked, the locomotor stimulant effects of alcohol were completely abolished in zebrafish.
These key findings are similar to those found in rodents and humans. However, studying how alcohol affects the brain is not enough. Since only a small proportion of individuals who consume alcohol develop addiction, research has to focus on these subset of individuals.
Individual sensitivities to alcohol's locomotor stimulant effect
Similar to humans, zebrafish also exhibit individual differences in their sensitivity to the effects of alcohol. The Gerlai research group at the University of Toronto Mississauga recently identified a subset of zebrafish within the general population that exhibit elevated anxiety-like behavioral responses. These fish also exhibited elevated brain tissue levels of the neurochemical serotonin [2].
Interestingly, experimentally induced stress can increase anxiety-like behavioral responses and reduce serotonin metabolism in zebrafish [3]. In humans, serotonin is highly implicated in anxiety, depression and addiction. However, what was most intriguing was that fish with elevated anxiety-like responses exhibited a potentiated response to alcohol's locomotor stimulant and anxiolytic (i.e. anxiety reducing) effects.
This discovery may help explain why certain individuals are more sensitive to the effects of alcohol and may be at a higher risk for the development of alcohol addiction. The mechanisms underlying alcohol addiction in humans are still not fully understood, but the above example demonstrates how using model organisms, including the zebrafish, may yield insights into this debilitating disease.
References
- Nowicki M.; Tran S.; Chatterjee D.; Gerlai R. (2015). Inhibition of phosphorylated tyrosine hydroxylase attenuates ethanol-induced hyperactivity in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Pharmacol Biochem Behav, 138, 32-39.
- Tran S.; Nowicki M.; Muraleetharan A.; Chatterjee D.; Gerlai R. (2015). Neurochemical factors underlying individual differences in locomotor activity and anxiety-like behavioral responses in zebrafish. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry, 65, 25-33.
- Tran S.; Nowicki M.; Fulcher N.; Chatterjee D.; Gerlai R. (2015). Interaction between handling induced stress and anxiolytic effects of ethanol in zebrafish: A behavioral and neurochemical analysis. Behav Brain Res, 298, 278-285.
Get the latest blog posts delivered to your inbox - every 15th of the month
more

How zebrafish and optogenetics are great for investigating stress
By this point, we do not need to tell you how popular zebrafish are. We also probably do not need to point out the great technological advances that are being made in research because of the use of optogenetics.
Zebrafish help us to understand neurodegenerative and neuromuscular diseases
Teresa Capriello and colleagues use zebrafish to study the neuronal mechanisms of heavy metals in connection to neurodegenerative and neuromuscular diseases.